The Hibernate architecture includes many objects such as persistent object, session factory, transaction factory, connection factory, session, transaction etc.
The Hibernate architecture is categorized in four layers.
- Java application layer
- Hibernate framework layer
- Backhand api layer
- Database layer
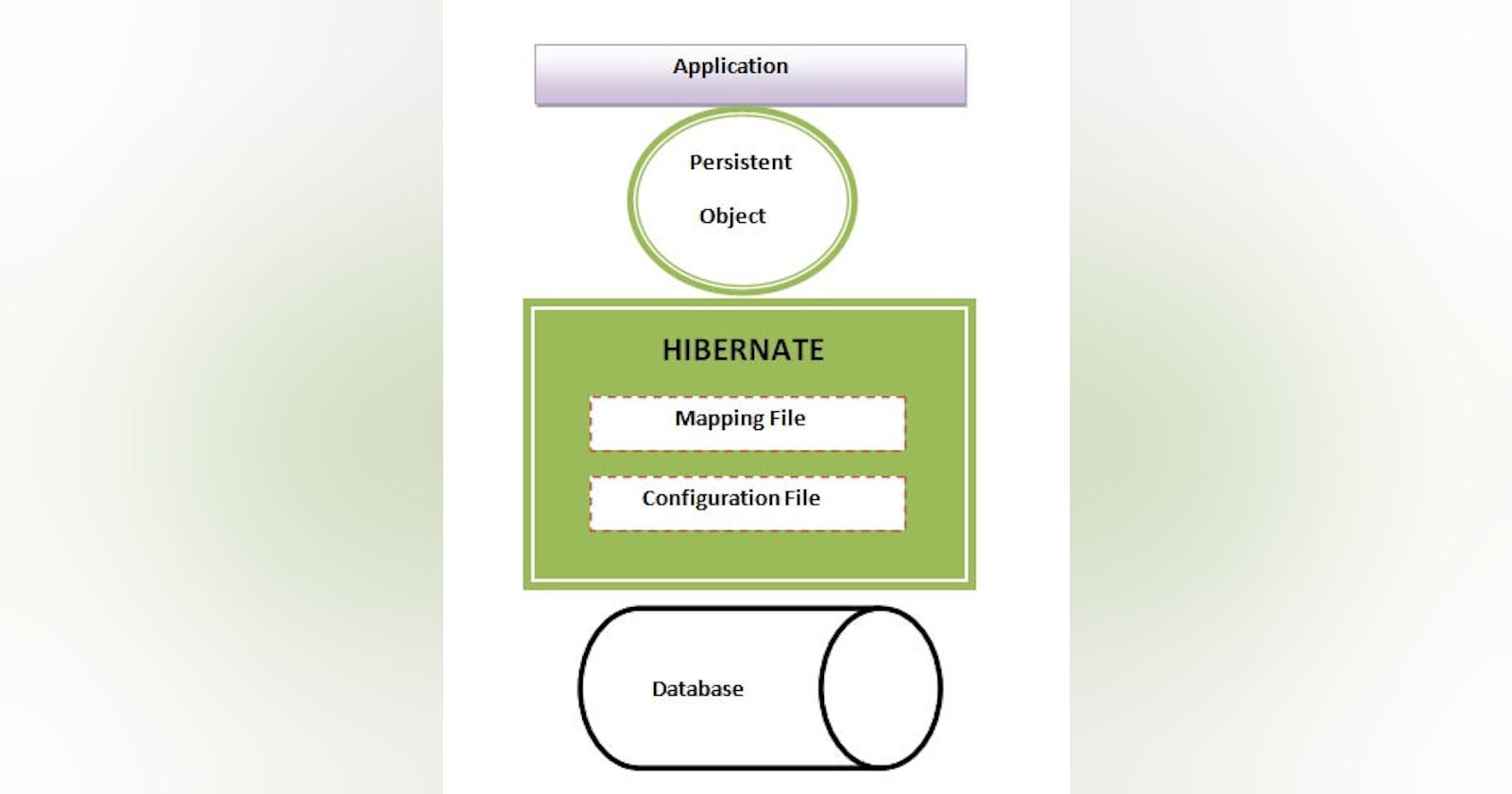
Let's see the diagram of hibernate architecture:
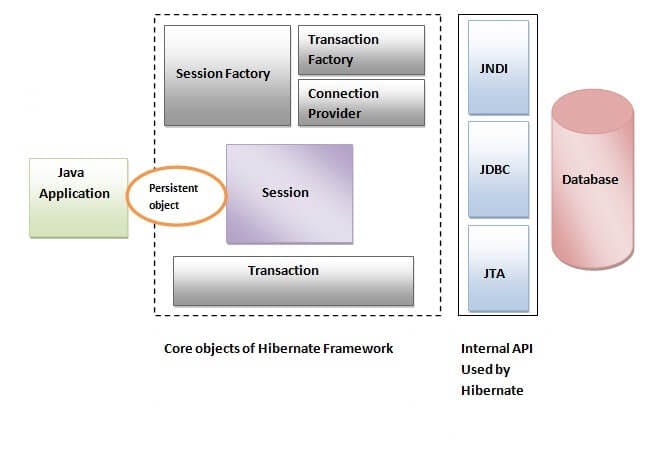
Hibernate framework uses many objects such as session factory, session, transaction etc. alongwith existing Java API such as JDBC (Java Database Connectivity), JTA (Java Transaction API) and JNDI (Java Naming Directory Interface).
Elements of Hibernate Architecture SessionFactory
The SessionFactory is a factory of session and client of ConnectionProvider. It holds second level cache (optional) of data. The org.hibernate.SessionFactory interface provides factory method to get the object of Session.
Session
The session object provides an interface between the application and data stored in the database. It is a short-lived object and wraps the JDBC connection. It is factory of Transaction, Query and Criteria. It holds a first-level cache (mandatory) of data. The org.hibernate.Session interface provides methods to insert, update and delete the object. It also provides factory methods for Transaction, Query and Criteria.
Transaction
The transaction object specifies the atomic unit of work. It is optional. The org.hibernate.Transaction interface provides methods for transaction management.
ConnectionProvider
It is a factory of JDBC connections. It abstracts the application from DriverManager or DataSource. It is optional.
TransactionFactory
It is a factory of Transaction. It is optional.